
25 May Why do you need enterprise cloud security?
Why do you need enterprise cloud security?
Businesses are largely spending on cloud services, but not as much on their security preparedness. A recent survey has shown that when businesses spend around $10 million on cloud services, only one-third of this spending were ensuring the security of cloud resources.
What is enterprise cloud security?
Enterprise cloud security is the process by which an organization protects its data, servers, workstations, storage, networking, applications, and every information asset in the cloud. An effective enterprise cloud security in today’s cyber setting is imperative to secure the public/private/hybrid/multi-cloud infrastructure on which the enterprise is built.
What are the different cloud security issues faced by enterprises?
You can say that in general, the basic cloud security challenges enterprises face is:
- Lack of understanding of what needs to be addressed
- Creating the framework to face the issues
Automation is becoming unavoidable and the cloud environment is rapidly evolving. This has made the upgrading of cloud framework a mandatory business measure.
Coming to the specific issues businesses are facing, data breaches are the primary cloud security challenge enterprises face. Cloud misalignments are causing data breaches in businesses, which further leads to phishing and identity theft. This way cloud providers and cloud platforms become vulnerable to several data endangerment risks.
Cyber attackers and hackers are becoming more sophisticated, making strategizing, implementing, or maintaining cloud security a huge challenge. Security complexity is rising due to these intrusions by cyber attackers and is largely causing business distress.
Also, insider threats are giving enterprises lots of botheration. Weak internal configurations and insecure APIs are causing cloud vulnerabilities and data loss.
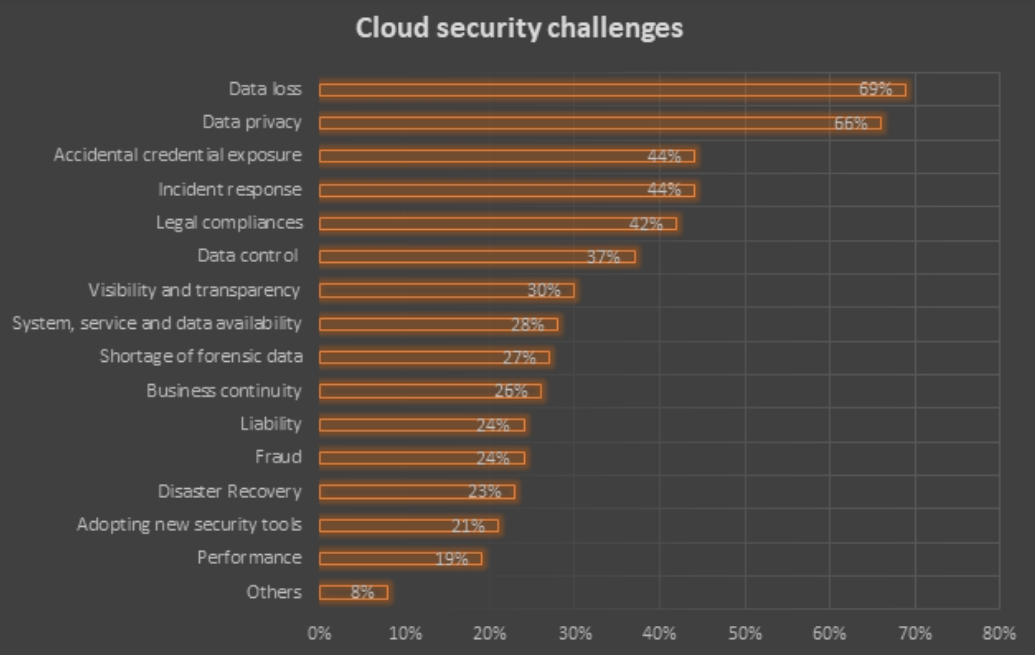
An online survey was conducted recently on around 650 cybersecurity professionals. 69% of the respondents said that data loss was the primary concern and 66% respondents shared data privacy as their main concern
Following were the other cloud security challenges businesses faced:
These cloud security issues necessitate the need for enabling enterprise cloud security solutions. But there are other reasons as well which require organizations to strengthen their enterprise cloud security measures. Let’s see what those are and why cloud security is an important aspect for any business.
What makes cloud security important?
In a recent survey, 83% of cloud technology experts pointed out that the biggest challenge of using cloud computing technologies in their organizations was related to cloud enterprise security. Other challenges included managing cloud spend, enterprise cloud security governance, and lack of expertise.
Cloud security for enterprise needs to maintain a strong posture to reduce upfront, operational and administrative costs, and improve scalability, reliability, and accessibility. Even though the cloud is a very critical business requirement, it is not risk-free. Lack of ideal cloud security practices can lead to significant fund outflows. Hence enterprises need to have cloud security practices in place.
Experts recommend that the teams should sharpen the following skills to stay on top of cloud security:
- Application Program Integration (API) and Command Line Interface (CLI) tools
- Cloud identity
- Container security
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) as a working process
How to implement a cloud security system?
Businesses need to have a bird’ eye view of cloud security strategies. So, how can enterprises identify pain points upfront, and fix them before the attackers can exploit them? Here is the step-by-step guide to cloud security best practices:
Phase #1: Cloud monitoring
Cloud usage and its corresponding risk assessment is the primary and most crucial phase in the implementation of the cloud security process. Enterprises need to see to it regularly by achieving the following steps:
- Identify sensitive or regulated data using data classification engines. This will avoid regulatory penalties or loss of intellectual property rights leading to data loss.
- Track who is accessing the sensitive data by evaluating permissions on files and folders in your cloud environment.
- Discover the availed cloud services that you are unaware of. Run risk profile assessments using a web proxy or SIEM logs.
- Your IaaS ecosystem will have many vulnerabilities arising from misconfigurations. Audit configurations, safeguard network configuration and encryption.
- Reduce data loss occurring due to careless employees or outside attackers. User Behavior Analytics (UBA) can be deployed to expose such mistrustful user behaviors in the enterprise.
Phase #2: Cloud protection
Now that you have monitored the cloud setting and understood the risk posture, the next step would be meeting these security issues with solutions and protective measures.
- Classify data as sensitive or regulated and assign data protection policies to decide on which data is to be stored/removed/isolated in the cloud.
- Encrypt your data from a third party. Make sure that you use your own keys so that the cloud service providers will not have access to your sensitive data.
- Enable data sharing controls by applying access control policies. You can start by changing control settings to viewer/editor modes and restricting the kind of data that can be shared externally through links.
- Avoid creating blind spots for your security posture by accessing cloud services from unmanaged devices. Enable device security verification before downloading data from the cloud.
- Azure and AWS offer anti-malware technology to the IaaS settings for protecting the infrastructure. For single-purpose workloads, you can deploy application whitelisting and memory exploit prevention. For general-purpose workloads, machine Learning-based protection can be deployed.
Phase #3: Cloud security incident response
The final phase in cloud security implementation is the quick reaction to incidents. When there is an incident, the teams have to provide either an automated or channeled response systematically. These are some of the best practices for cloud security incident response:
- Enable additional verification practices like two-step authentication for proving identity when a user tries to access highly sensitive data from a new device
- Integrate cloud risk database with secure gateways/firewalls for automatically updating web access policies. This way you will have a warning message when a risk profile tries to access the cloud data. You will be able to deny access or block the risk profiles immediately by opting for such cloud access policy adjustments.
- Remove malware from the cloud ecosystem by scanning your files. Malware can risk files in a shared folder by automatically synchronizing with a cloud storage service. Scanning files and removing malware can avoid ransomware threats and data breaches.
Conclusion:
In a recent survey, 60% of the respondents said that enterprise downtime can cost a business between 3m$ to 5m$ per hour. The margin of IT issues is extremely thin. In the wake of increasing enterprise cloud security issues, businesses should understand that such disruptions can have a shattering impact on businesses like financial and reputational damages. Enterprises must be purpose-built to provide uptime SLAs and data security while availing the cloud services. However, lately, we are seeing efforts taken by cloud-managed services to offer assurances that the enterprises’ systems and data are secure
